UNIT 4 |
CKD Diet
Diets commonly consumed in Western countries are important contributors to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and its progression. The Western eating pattern is high in calories, dietary acid and saturated fat from animal products, sodium, phosphorus, and refined sugars, and low in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and other foods high in fiber and antioxidants. Such Western diets contribute to hypertension, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia that can lead to CKD. Patients with progressive CKD also commonly present with malnutrition, which calls for a meal plan high enough in calories to prevent excessive weight loss.
The right kind of diet, as described below, can help reduce progression of CKD, control blood pressure and cholesterol, and may prevent cardiovascular events. The following dietary factors are clinically significant in patients with CKD. Loss of Excess Weight. Obesity is an independent risk factor for the development and progression of CKD. Both dietary and surgical interventions that promote loss of excess weight reduce proteinuria and blood pressure. Other obesity-related diseases, including metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, are also significantly associated with microalbuminuria, proteinuria, and an increased risk for CKD. However, among patients with established CKD, obesity is associated with greater survival.
The right kind of diet, as described below, can help reduce progression of CKD, control blood pressure and cholesterol, and may prevent cardiovascular events. The following dietary factors are clinically significant in patients with CKD. Loss of Excess Weight. Obesity is an independent risk factor for the development and progression of CKD. Both dietary and surgical interventions that promote loss of excess weight reduce proteinuria and blood pressure. Other obesity-related diseases, including metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, are also significantly associated with microalbuminuria, proteinuria, and an increased risk for CKD. However, among patients with established CKD, obesity is associated with greater survival.
Protein-energy wasting (PEW) is associated with poor clinical outcome and mortality in CKD and is multifactorial. Although reduced food intake due to anorexia and dietary restrictions are obvious contributors, uremia-induced alterations such as increased energy expenditure, persistent inflammation, acidosis, and endocrine changes such as lower levels of testosterone and thyroid hormone, resistance to insulin, growth hormone (GH), and IGF-1, and elevated levels of glucocorticoids are also significant contributors. Although correct implementation of protein-restricted diets does not induce protein-energy wasting, a relaxation in dietary restriction is warranted for patients with a significant degree of PEW.
Food Preparation
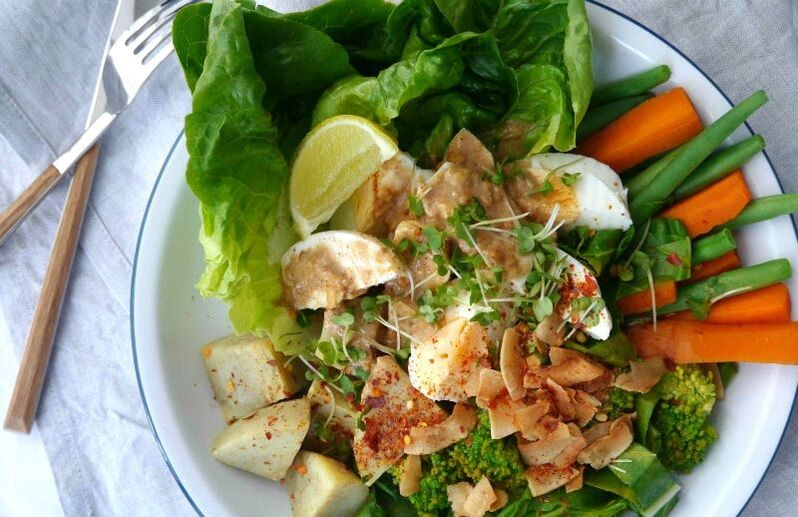
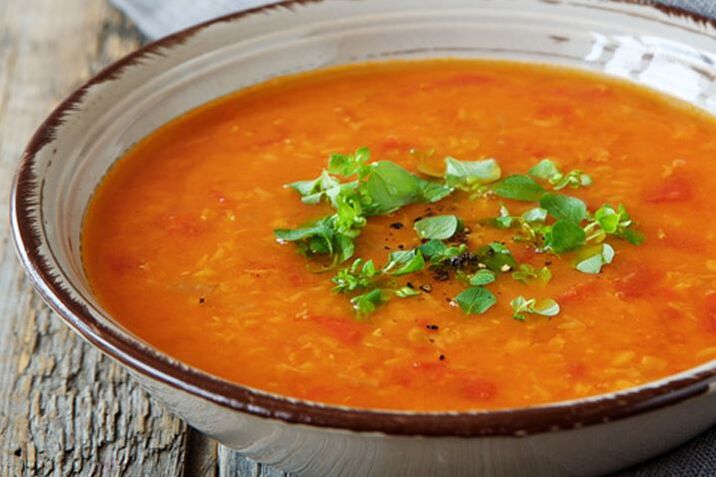
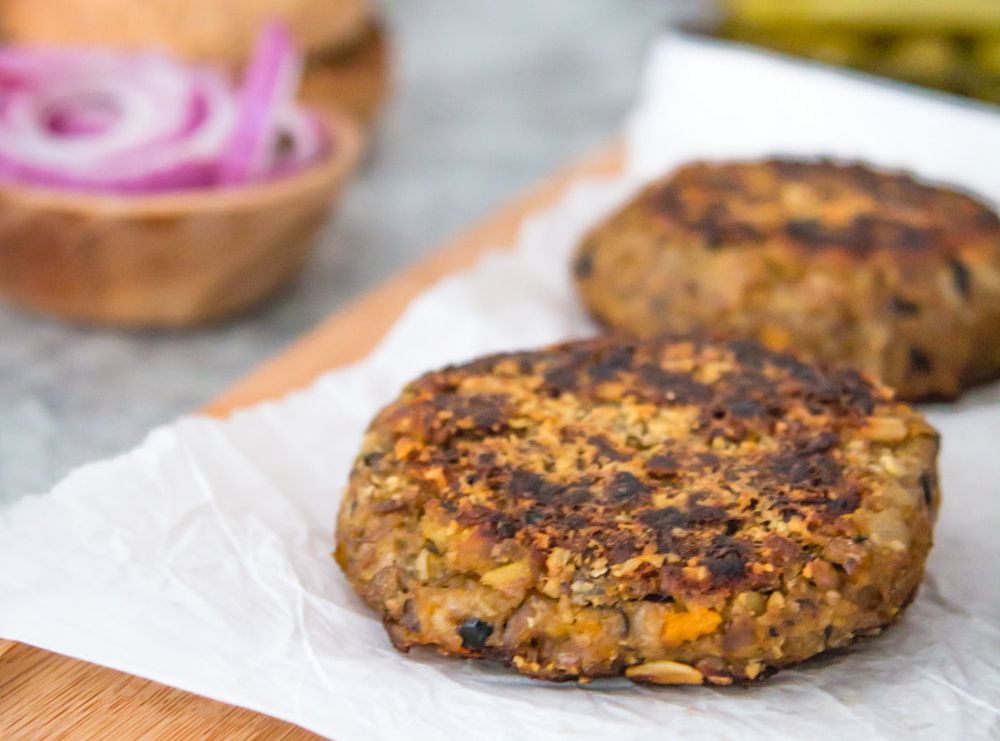
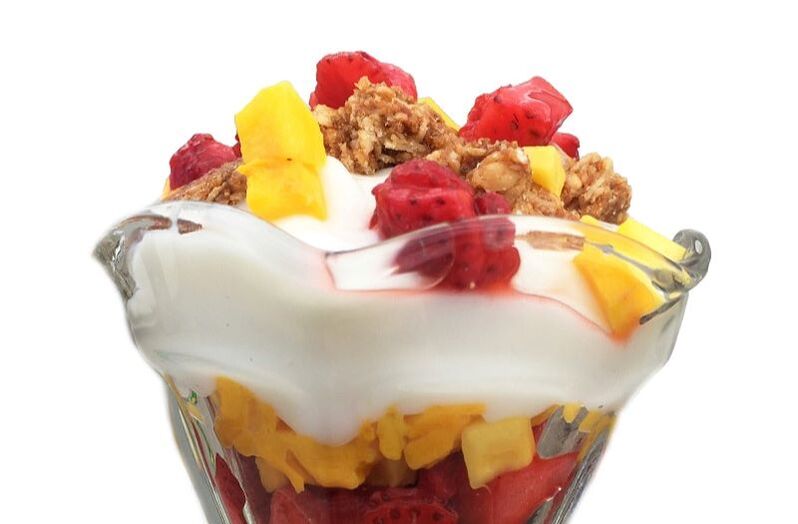
You may access all the recipes listed below. Choose one recipe in each category and create 1 set of meal course that you can recommend to patients/clients or your family member. All recipes have instructions that you may also use as guide. Document your activity by taking photos of each recipe, starting from Mise en place up to the final presentation with brief description of your planned meal.
|
.
|
Unit Task
Please organize your documentation in a single file and send us the completed task using PDF format.